TABLE OF CONTENTS
The global robotics industry, estimated to be worth around $46 billion, has been projected to expand to $169.8 billion by 2032. How do we explain the surge in revenue, and what are the main drivers behind the spike in demand?
McKinsey & Company estimates that retail and consumer goods will be the biggest spenders within the industrial sectors over the next five years. Although robots won’t be selling customers the finished product (yet), they will automate the sorting, handling, and palletization of material goods as they’re assembled in the production process.
In this article, we’ll briefly explain the robotics industry, break down today’s top robotics trends, the market’s challenges, and the future implications of the trends we’re spotting. Additionally, we’ll show how PLM software (product lifecycle management) can best help your robotics company navigate these trends.
What defines the robotics industry?
The robotics market involves the design, development, manufacturing, and deployment of robots—machines programmed to perform tasks autonomously or with minimal human intervention. In 2024, the United States was tipped to generate the highest revenue in the world at $784.6 billion, the main contributor being high customer demand for automation solutions. This surge is due to robots’ ability to automate tasks that are too dangerous, expensive, or monotonous for humans.
Robots are increasingly used in manufacturing to improve precision and safety. They perform tasks like welding, material handling, assembly, painting, machine tending, and quality inspection with high accuracy and consistency. Robots also aid in cutting, machining, and packaging, automating processes to increase speed and reduce errors. By handling heavy lifting and transport, robots can make the workplace safer and reduce the risk of injury to workers on the factory floor.
Rapid Robotics is addressing these needs by automating repetitive manufacturing tasks such as part handling, inspection, and pad printing using reusable robots offered as a service. Rapid Robotics’ approach reduces costs and deployment times, allowing manufacturers to implement automation without large upfront investments.
Top robotics industry trends
Robots are becoming automous becuase of AI + ML
The way robots are being trained is fundamentally changing. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are being used to make robots more autonomous. Robots are now being programmed with a generative AI-driven interface–that uses human language instead of code.
Autonomous robots are designed to operate independently and can be used in manufacturing, logistics, and healthcare. Their primary focus is on automating tasks that would otherwise require human labor.
The advantages of using AI + ML in robot manufacturing range from more efficient algorithms to more predictive maintenance. More data can be crunched faster, allowing for continuous optimization. Predictive AI reduces downtime by anticipating maintenance needs, helps robots increase adaptability and performance, and learns from their surroundings.
Two robotics companies that excel at designing autonomous robots using AI and ML include Locus Robotics and Monarch Tractor:
Locus Robotics uses AI and ML to augment their warehouse robots, which assist in picking and transporting items within fulfillment centers. Their robots autonomously navigate through warehouses, improving order fulfillment efficiency.
Monarch Tractor applies AI and ML to make autonomous tractors for farming. They built the world’s first fully electric tractor, a driver-optional, autonomous tractor using AI to navigate fields and manage crops more efficiently.
New education and training programs are being developed to close the automation skill gap
The robotics industry faces a skills gap, as the current workforce lacks the expertise to implement and manage automated robots. Although this has led to a labor shortage, one way to address this is by making robots more accessible through targeted education and training programs to equip workers with the right skills.
Technological advancements have been outpacing current educational and training frameworks. Workers often find themselves unprepared to handle modern robotic systems, from programming to maintenance. This discrepancy delays automation adoption and worsens the labor shortage as companies struggle to find qualified personnel.
Solving this issue requires updating educational curricula to include advanced robotics and automation technologies. Industry partnerships can provide hands-on training and real-world experience through internships and apprenticeships. Ongoing professional development programs can help current workers upskill, ensuring they stay competent as technologies evolve.
iRobot is already active in this area with STEM programs and initiatives to teach kids about coding and robots. Their STEM Outreach program partners with schools and organizations to offer robotics and coding resources, including curriculum materials, workshops, and participation in competitions like FIRST Robotics. The Create® 3 Educational Robot helps students learn through hands-on activities and challenges.
The government is also actively incentivizing workers’ upskilling to manage robotic systems. National Science Foundation (NSF) programs, such as Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) and Foundational Research in Robotics (FRR), are funding research to advance robotics and automation technologies. The ARM Institute’s Apprenticeship Program focuses on training workers for careers in advanced robotics and manufacturing.
These governmental programs aim to create a skilled workforce to manage and work with robots. As automation integrates into more sectors, a well-trained workforce will be key to maintaining competitiveness and innovation. Prioritizing these initiatives will help to build a bigger pipeline of skilled professionals and solve the labor shortage.
Cobots are collaborating more with humans and becoming more humanoid
What are Cobots?
Cobots are collaborative robots that work with humans in shared spaces for tasks like heavy lifting and repetitive motions. They are equipped with advanced sensors and vision technologies to safely interact with us in the workplace without putting us in danger. These sensors enable cobots to detect and respond to human presence, movements, and actions in real time. This ensures robots don’t inadvertently injure a human in the assembly line.

Qingdao University researchers’ newly developed touch sensor proves this trend in action. Unlike traditional sensors that need direct contact to notify the robot, this technology senses changes in the electric field between an object and the sensor, working even at distances of up to 100 millimeters. This non-contact approach, combined with the sensor’s high sensitivity and response time, means cobots and humans can work together more in the future.
RightHand Robotics, Inc. has been designing cobots since 2015. The company develops robotic piece-picking solutions that work with humans in warehouses and fulfillment centers. In 2018, it won a world record for the fastest piece-picking robot.
Another company leading the robotics industry in cobot production is Apptronik. Apptronik’s core mission is to build robots that are teammates for humankind. They’re focused on developing general-purpose humanoid robots for facility inspections, Supply chain operations, and other labor-intensive or dangerous tasks.
Advancements in cobot technology have applications that extend beyond just the robotics industry. The development of humanoid robots that resemble and move like humans can one day be used in healthcare, hospitality, and customer service.
AR & VR create cheaper and safer environments for training robots
Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) are immersive technologies that augment our perception of the world. AR overlays digital information onto the real world, while VR creates simulated environments.
AR and VR are changing how robots are designed, operated, and maintained. For example, AR headsets can provide technicians with real-time data and instructions overlaid onto their view of the physical robot, simplifying complex tasks like troubleshooting and repairs.
VR simulations offer a safer and less expensive environment for training robot operators, allowing them to practice in realistic scenarios without the risk of damage or injury. AR and VR also control teleoperated robots, allowing operators to remotely control robots in hazardous environments, such as space or disaster zones.
Companies using AR and VR in Robotics
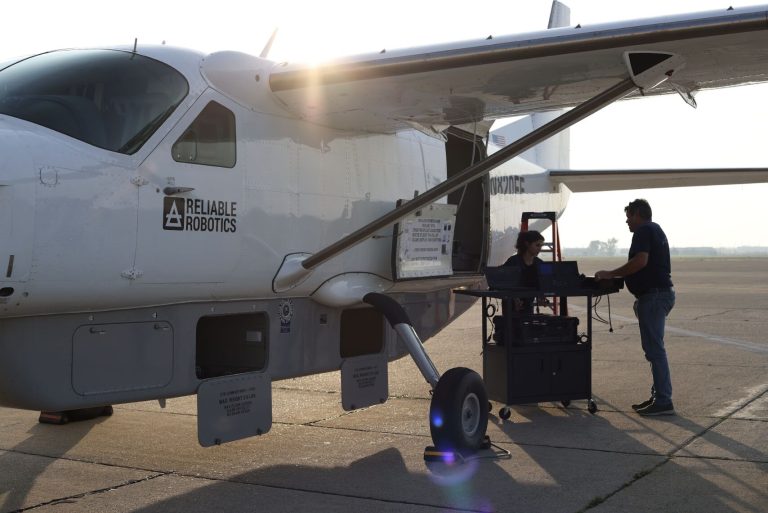
Reliable Robotics Corporation automates aircraft operations and leverages AR and VR to create realistic simulations for training pilots and ground crews in takeoff, landing, and emergency procedures. This approach enhances training effectiveness and safety, making aviation operations more reliable and efficient.
Extend Robotics developed a VR-based interface enabling users to remotely control robotic arms for in-space manufacturing, including repairing satellites and fuel tanks. By merging VR and robotics, Extend Robotics mitigates the cost of having astronauts in space and broadens the scope of robotic tasks.
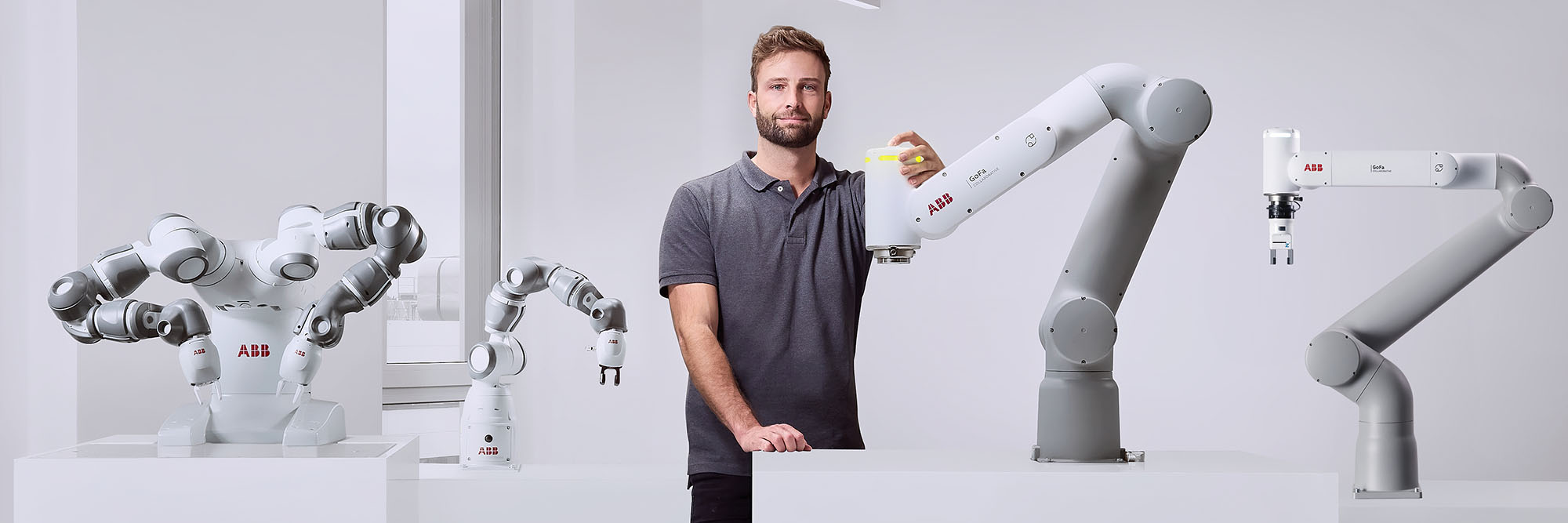
ABB Robotics uses augmented and virtual reality to enhance robotic system training and maintenance. These technologies enable remote diagnostics and streamline the design process, increasing efficiency and reducing downtime in industrial settings. ABB Robotics and Agilent Technologies are collaborating to enhance laboratory automation by integrating their technologies to expedite research and quality control across industries.
Digital twins are optimizing robot performance
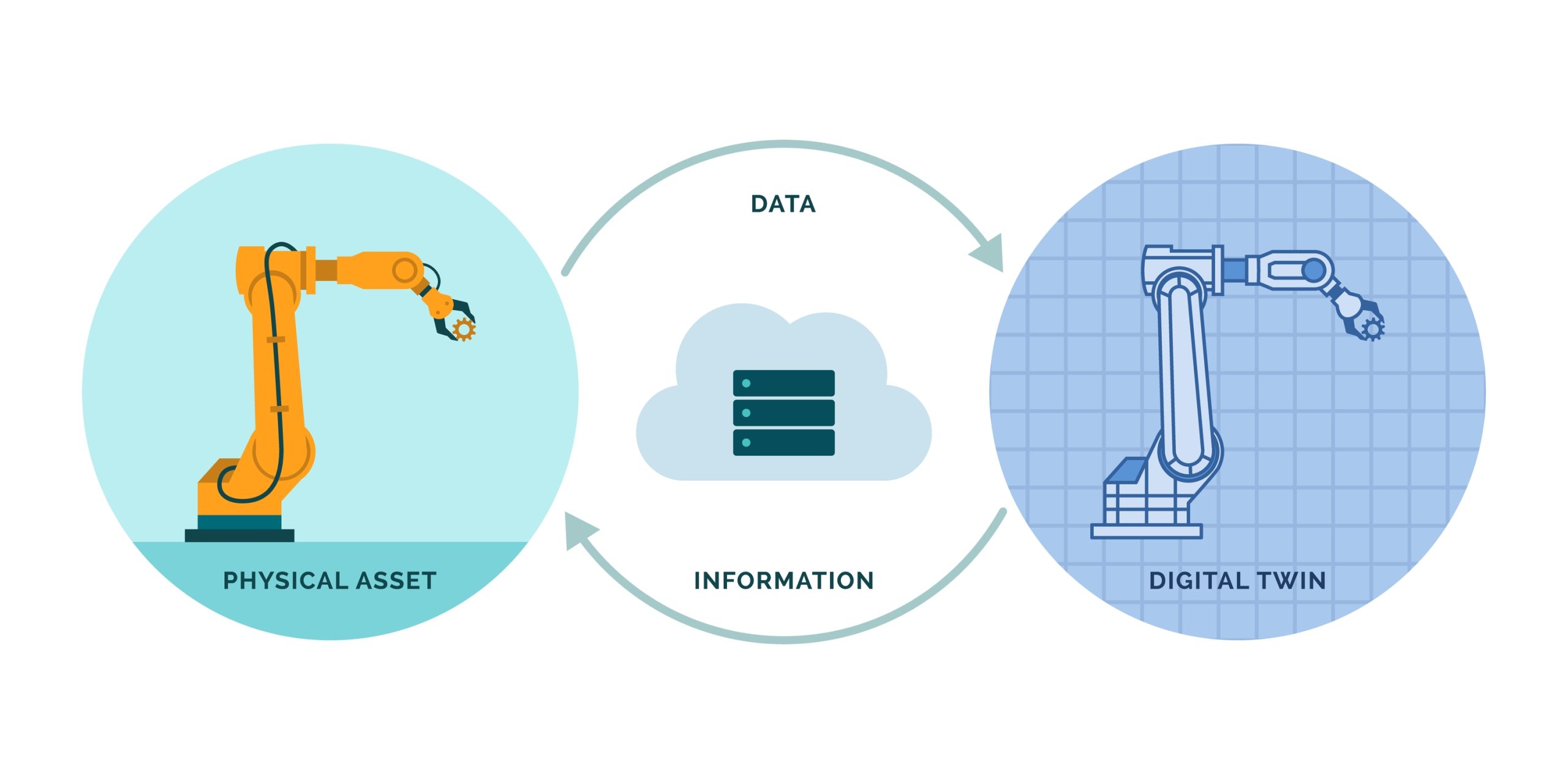
Digital twins are virtual replicas of physical systems that mirror their real-world counterparts in real-time. These models use data from sensors and machines to simulate the behavior and performance of their physical equivalents. By providing a detailed digital representation, digital twins allow for continuous monitoring, analysis, and optimization of the systems they replicate. This technology helps identify potential issues, tests changes without physical risks and empowers operators to make informed decisions.
How do digital twins work?
In the robotics industry, digital twins create a virtual model of a robot and its environment. This allows engineers to run simulations to predict outcomes, identify potential failures, and optimize performance before deployment. This capability helps reduce costs, enhance safety, and improve the efficiency of robotic operations.
Digital twins fine-tune processes like welding and painting in manufacturing and assembly lines, ensuring higher product quality and consistency. Companies can maximize the productivity and reliability of their robotic systems while minimizing downtime and risks by using digital twins.
In warehouse robotics, digital twins streamline operations by simulating scenarios to determine the most efficient routes, layouts, and processes. They also aid in predictive maintenance by monitoring the virtual replica’s condition for potential failures. Digital twins are valuable tools for training personnel and stakeholders in a safe, controlled environment.
What challenges does the robotics industry face, and how can PLM help?
High implementation costs and a lack of internal knowledge are major roadblocks to growth, especially for smaller robotics companies. The price of robots and automation systems, including setup and upkeep, can be astronomical, especially when the return on investment isn’t immediately clear. Many businesses lack in-house expertise to properly set up and manage these complex systems, potentially leading to costly errors and inefficient operations.
As a central hub for product information, PLMs identify cost-saving opportunities and improve their supply chains. PLM platforms eliminate manual entry and save engineers valuable time via direct integrations with manufacturing and engineering platforms like SolidWorks, Netsuite, and Tulip. PLM systems eliminate data silos and make it easier for teams to share designs. By breaking down data silos, teams can communicate more easily and efficiently.
Robotics companies without a PLM tend to implement dated and limited technologies that lack a single source of truth for their data. Juggling multiple platforms causes frustration and production delays when time-sensitive data is lost in the mix. PLM provides a unified platform for product data, addressing these challenges head-on.
Duro understands that robotics companies prioritize creating innovative designs above all else. As a leading PLM provider in the robotics sector, our platform minimizes administrative processes so your teams can focus on what truly matters: developing cutting-edge robotic solutions.
What do these trends mean for the robotics industry?
The robotics industry is witnessing advances in AI, machine learning, collaborative robots, augmented reality, and virtual reality. Robotics trends in 2025 highlight robots becoming more autonomous, new training programs to address skill gaps, and improved safety features for cobots.
AI and machine learning will make robots smarter and more versatile. Digital twins will improve robot performance and maintenance, while AR and VR will change how robots are designed and operated. As these technologies improve and get smarter, robotics will become increasingly important in making processes on the manufacturing floor more productive and safe.
With these advancements, product lifecycle management effectively manages product data and streamlines processes across the robotics industry. Integrating technologies like AI, ML, AR, and VR, PLM systems support today’s top robotics companies in innovating more quickly and efficiently. Agile PLM software helps optimize design, manage changes, and ensure compliance, helping to reduce costs and speed up time to market.