TABLE OF CONTENTS
The global aerospace industry is tipped to surpass $1 trillion by 2030, driven by innovative aerospace companies advancing next-generation spacecraft and propulsion systems.
Aerospace industry trends indicate a shift toward private investment, miniaturized satellites, and new launch technologies, shaping the future of space exploration and commercial flight.
This article highlights some of the top aerospace companies leading this transformation and how their cutting-edge solutions expand access to space, optimize defense systems, and advance commercial aerospace.
ispace
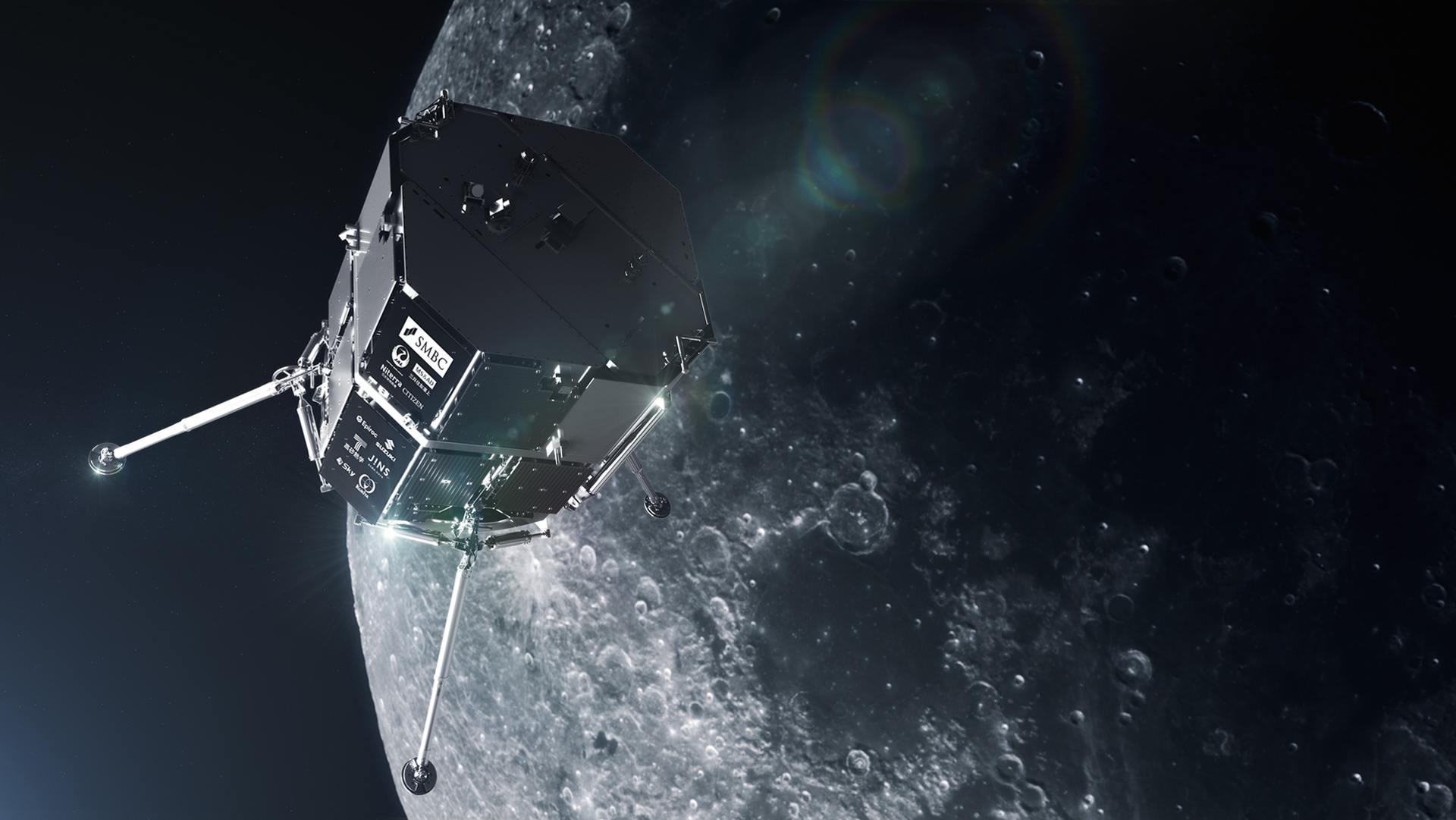

ispace is redefining lunar exploration with its “Hakuto-R” lander program, aiming to establish sustainable commercial activity on the Moon. ispace successfully launched its first lunar mission aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9, laying the groundwork for future resource utilization and long-term habitation. With plans for a second mission and NASA partnerships, ispace is a key player to keep an eye on in the lunar economy.
ABL Space
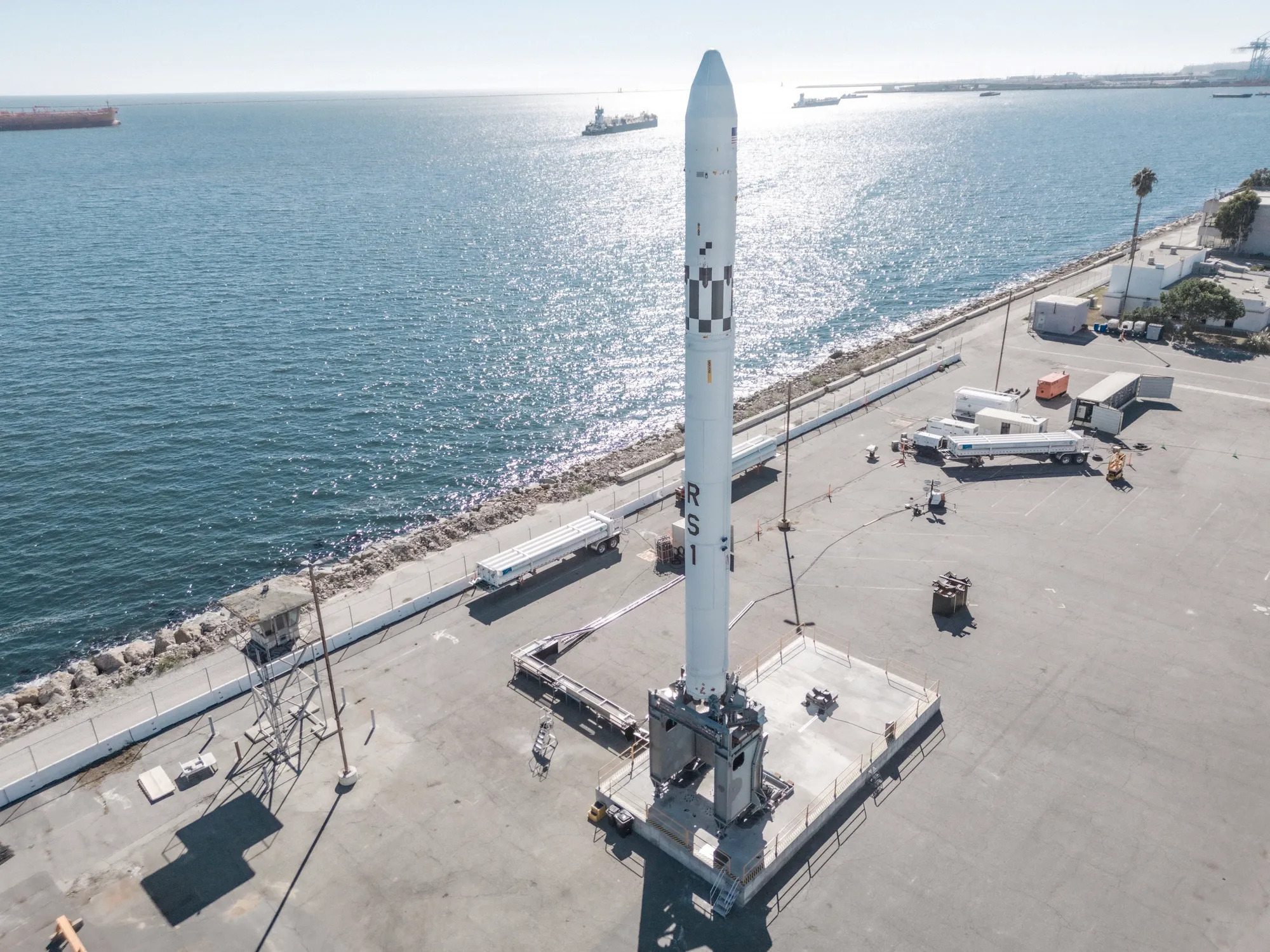
After initially developing the “RS1″ rocket and a mobile launch system, ABL Space Systems is now pivoting from commercial launch to missile defense, citing a shifting market and national security needs. Despite setbacks in RS1 test flights, ABL Space has raised nearly $500 million, including a $372 million Series B round, to develop its technology. With the DoD allocating $13.5 billion to missile defense in FY 2025, ABL Space aims to apply its expertise to responsive launch and advanced defense solutions.
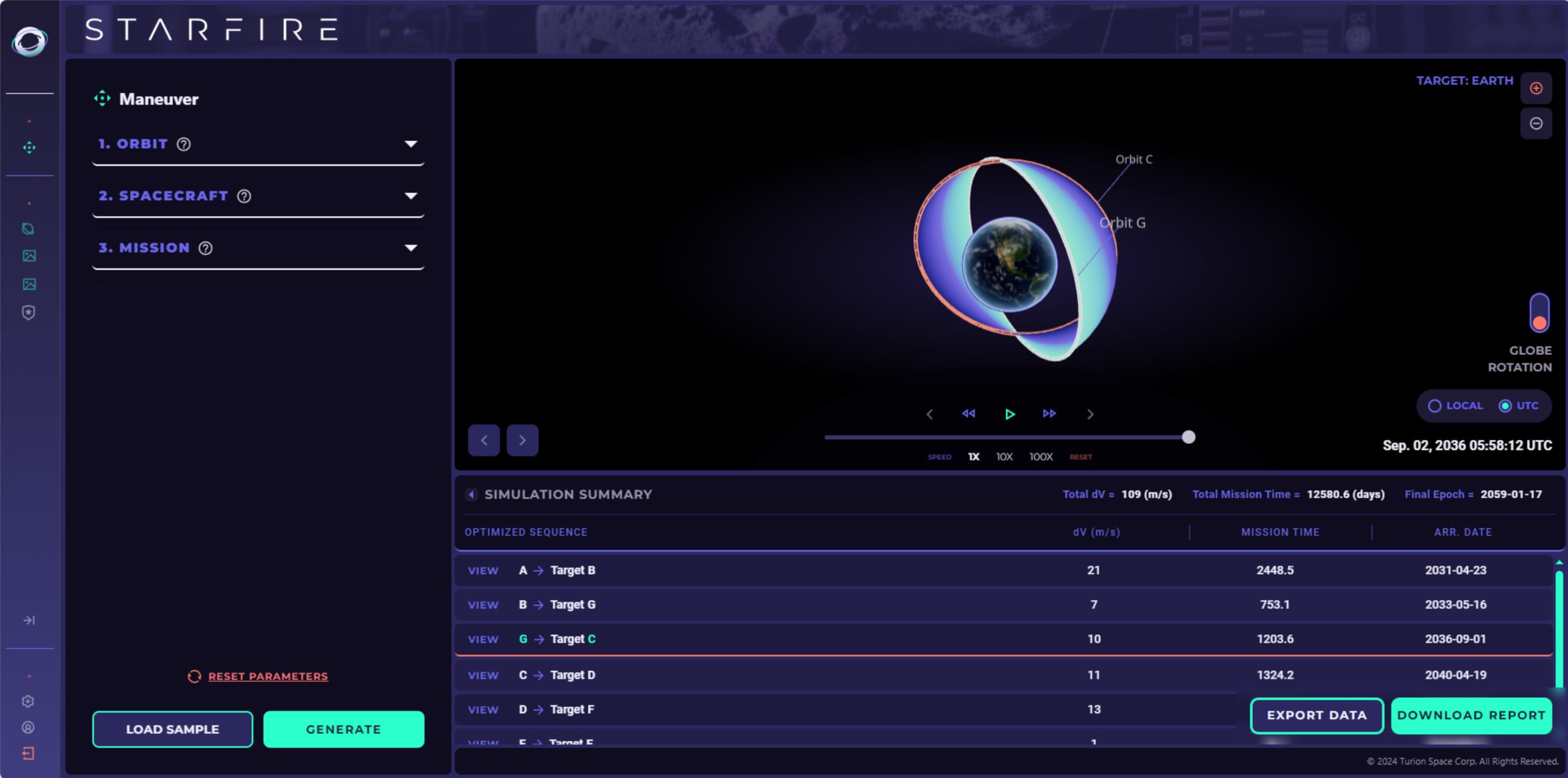
Turion Space
Turion Space is advancing orbital debris removal, satellite servicing, and space sustainability, developing solutions to track space objects, remove defunct satellites, and extend the life of active assets. Turion Space is now expanding its mission to support national security and space domain awareness. Turion Space recently secured a contract to build multi-payload satellites for the U.S. Space Force, enhancing orbital monitoring and defense capabilities.
EOI Space
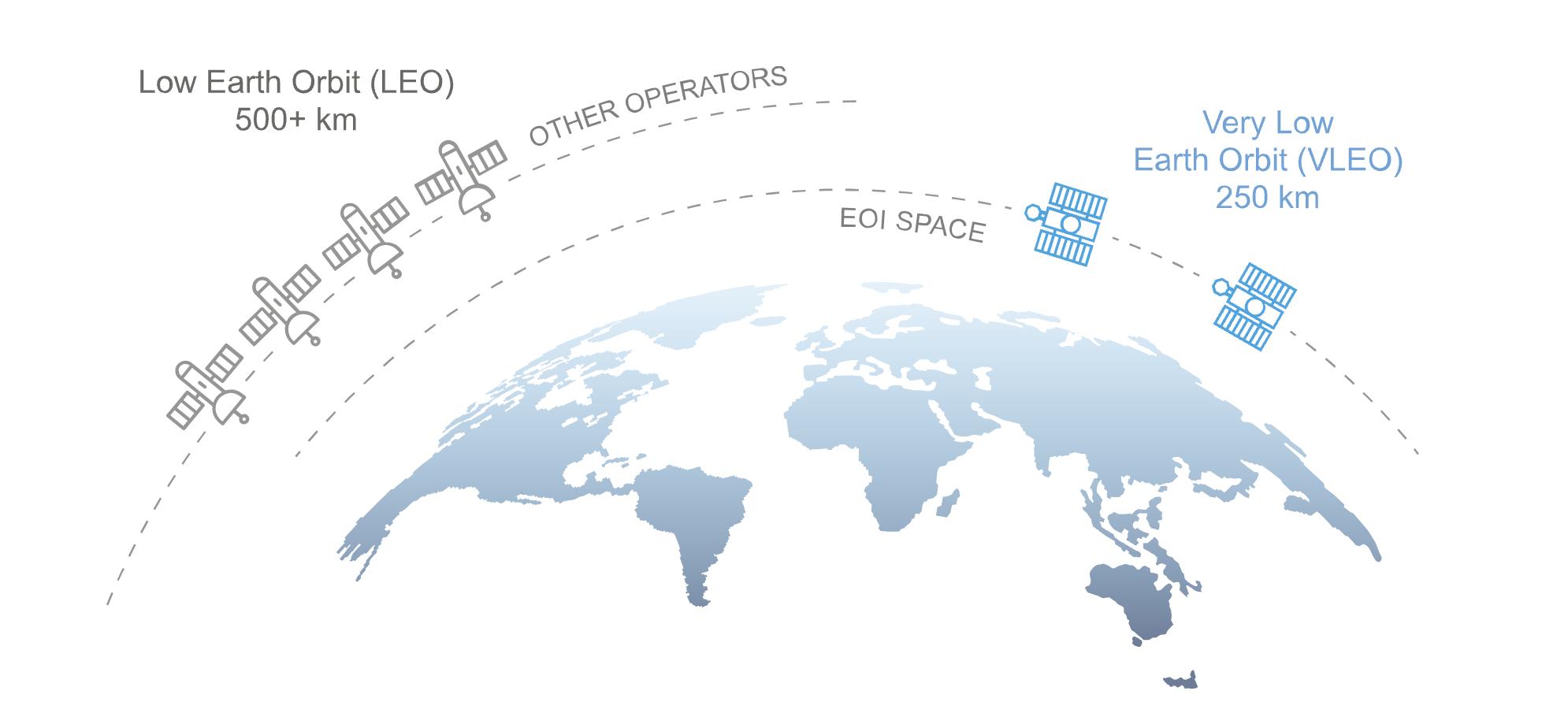
EOI Space is advancing Very Low Earth Orbit (VLEO) imaging with its “Stingray Constellation”, a network of high-resolution satellites providing real-time geospatial intelligence for the defense, insurance, and emergency response sectors. EOI Space’s technology will enhance natural disaster response by delivering instant, high-resolution imagery to assess damage, coordinate relief operations, and improve situational awareness. EOI Space has successfully tested its flight propulsion system, bringing it closer to deploying its advanced Earth observation capabilities.
Loft Orbital
Loft Orbital is re-thinking satellite deployment with its satellite-as-a-service model, enabling companies to launch payloads without building custom satellites. Its “YAM” series satellites support defense, climate monitoring, and Earth observation missions. Loft Orbital recently raised $170 million in Series C, bringing its total funding to $325 million to expand manufacturing, integrate AI into satellite operations, and scale its space infrastructure services.
AstroForge
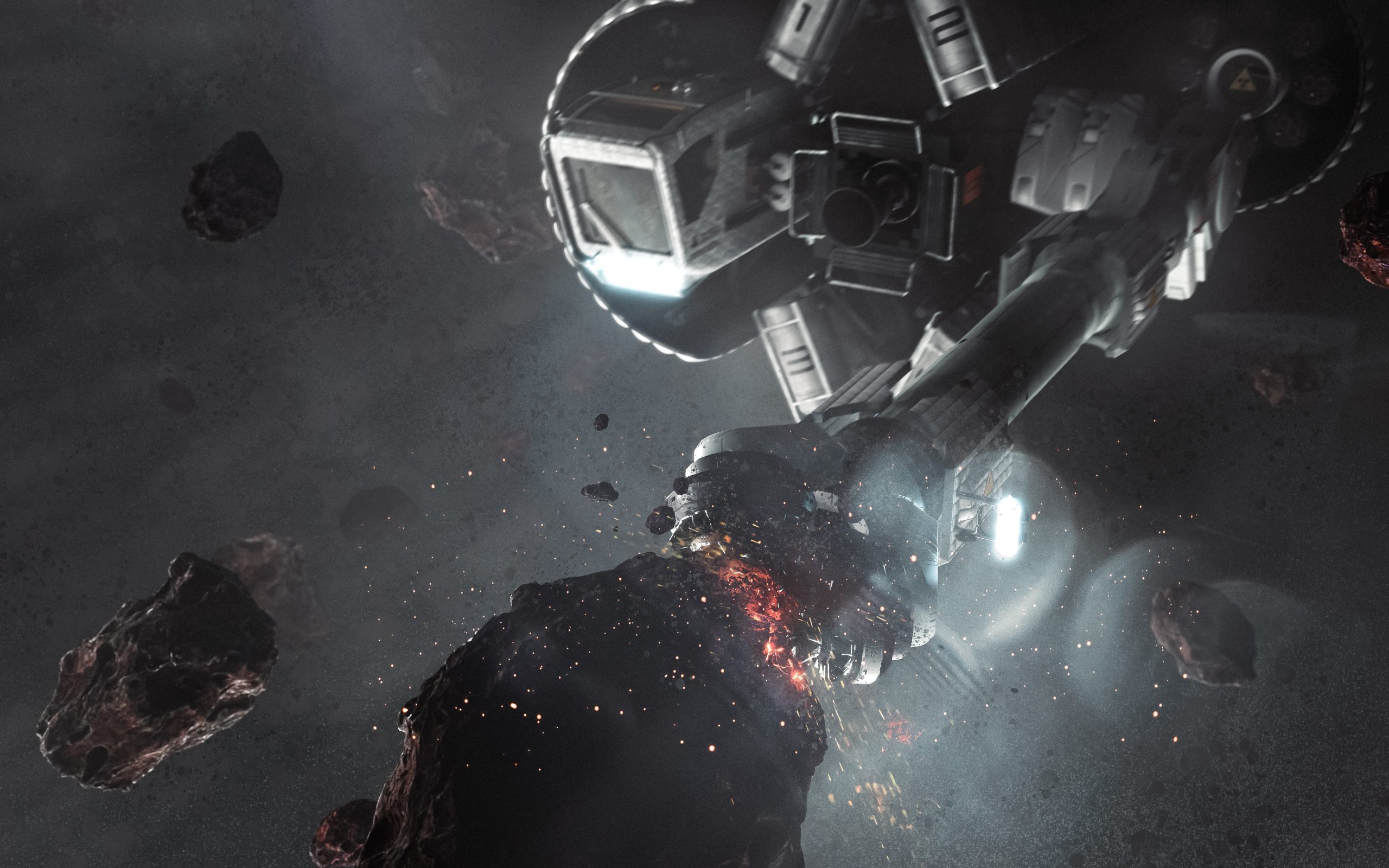

AstroForge is advancing space mining by extracting critical metals from asteroids, making off-world resources more accessible and cost-effective than traditional mining. AstroForge’s early 2025 “Odin” mission will test deep-space refining technologies and gather crucial data for future asteroid mining operations. Backed by $55 million in funding, AstroForge is scaling its capabilities, refining its extraction processes, and moving closer to making asteroid mining a commercially viable industry. AstroForge named its target asteroid “2022 OB5” and secured a multi-launch deal with Stoke Space to support future deep-space mining missions.
True Anomaly
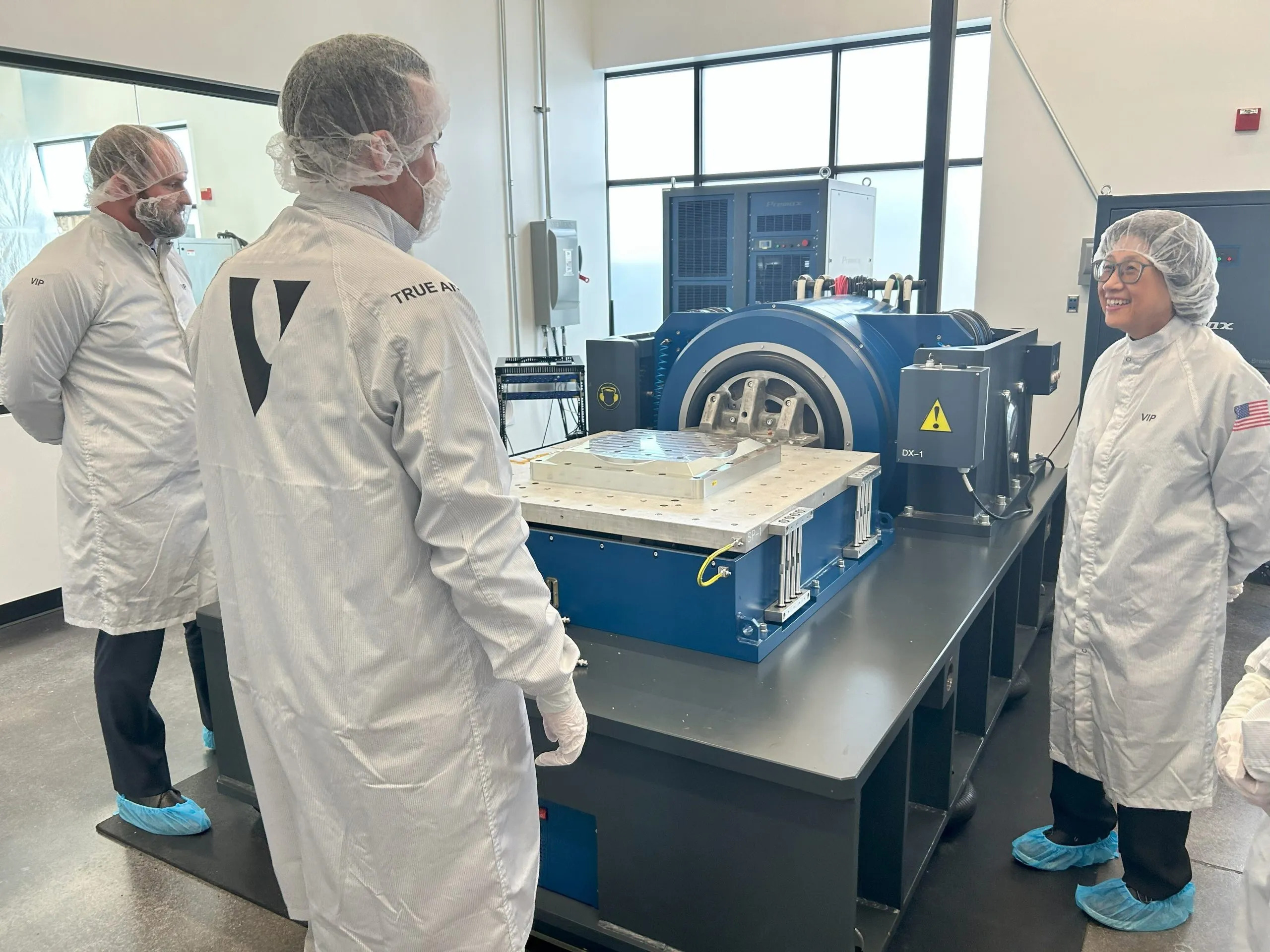
True Anomaly enhances space security and sustainability by developing advanced hardware and software solutions at the intersection of spacecraft, software, and artificial intelligence. Its Jackal Autonomous Orbital Vehicle (AOV) is designed for versatile on-orbit missions, including space domain awareness and satellite servicing. In December 2024, True Anomaly successfully launched and controlled its Jackal AOV during Mission X-2, showing how it can support real-time threat monitoring, maneuverability testing, and autonomous space operations.
Varda Space
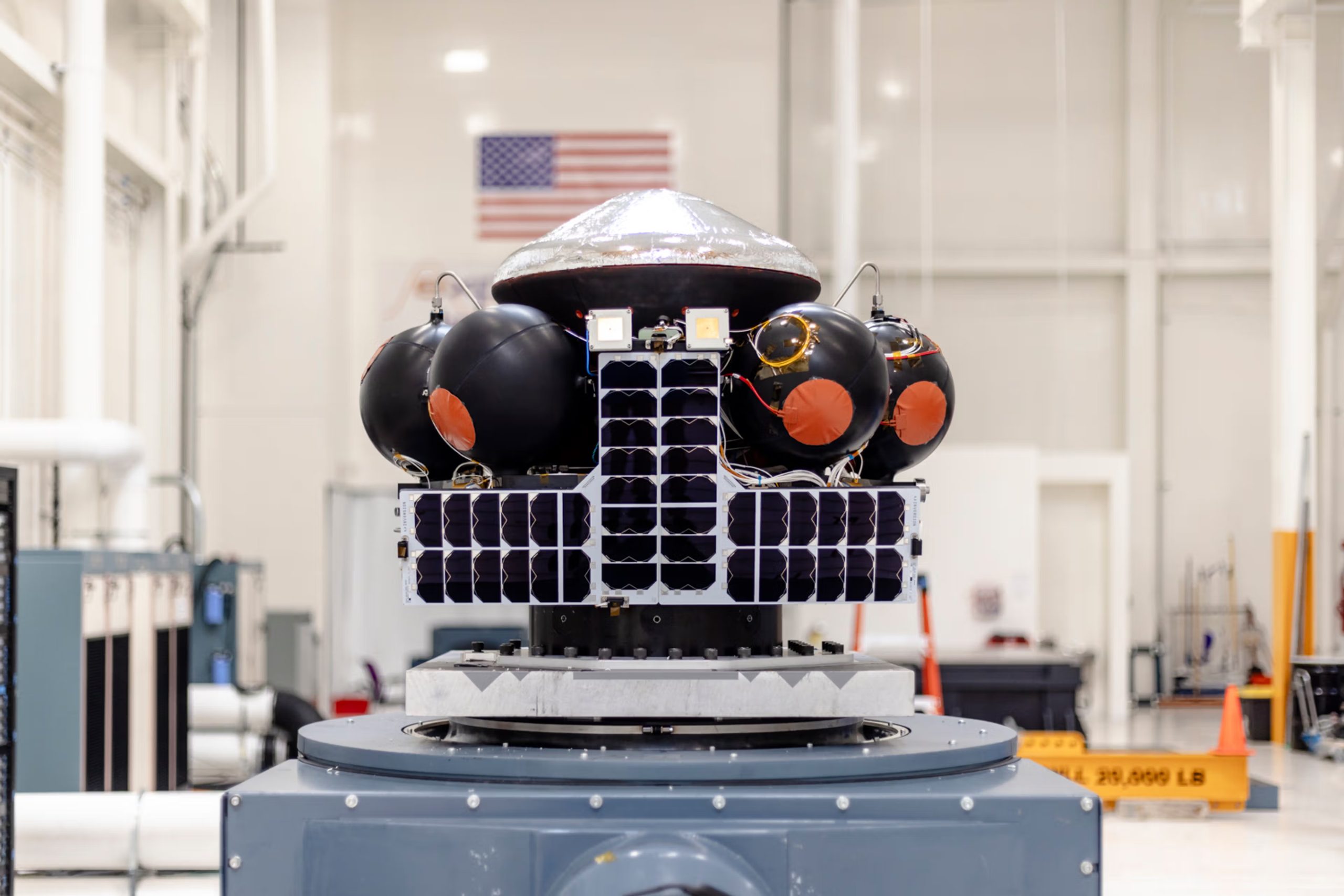
Varda Space Industries is advancing in space manufacturing, leveraging microgravity to produce high-value pharmaceuticals and advanced materials. Varda Space completed its first re-entry mission, proving the feasibility of space-based production and Earth return logistics. With growing partnerships in the biotech and semiconductor industries, Varda Space is set to commercialize space manufacturing. Rocket Lab recently delivered its third in-orbit manufacturing spacecraft for Varda, supporting its efforts to scale in-space production.
Inversion Space
Inversion Space develops orbital cargo delivery solutions with a capsule-based reentry system to quickly return materials from space. Its technology has applications in biomedical research, national security, and supply chain resilience. With $71 million in funding from Space Force, Inversion Space is advancing its “Arc” autonomous reentry capsule to deliver high-precision cargo to remote and strategic locations. Inversion Space launched its subscale pathfinder capsule, “Ray,” on SpaceX’s Transporter-12 rideshare mission, demonstrating its precision landing capabilities for future defense and commercial applications.
Vaya Space
Vaya Space develops orbital launch vehicles, in-space propulsion systems, and advanced missile engines, combining liquid bipropellant engines’ performance with solid rocket motors’ simplicity and reliability. Vaya’s propulsion system uses liquid oxidizer, solid fuel, and non-explosive, non-toxic propellants. Vaya Space uses 7.8 metric tons of recycled post-industrial plastic per launch to reduce waste and lower environmental impact. Vaya Space recently announced a multi-launch contract with Space Telecommunications to deploy up to 250 satellites using its “Dauntless” rocket, with launches set to begin in 2027.
Firefly Aerospace
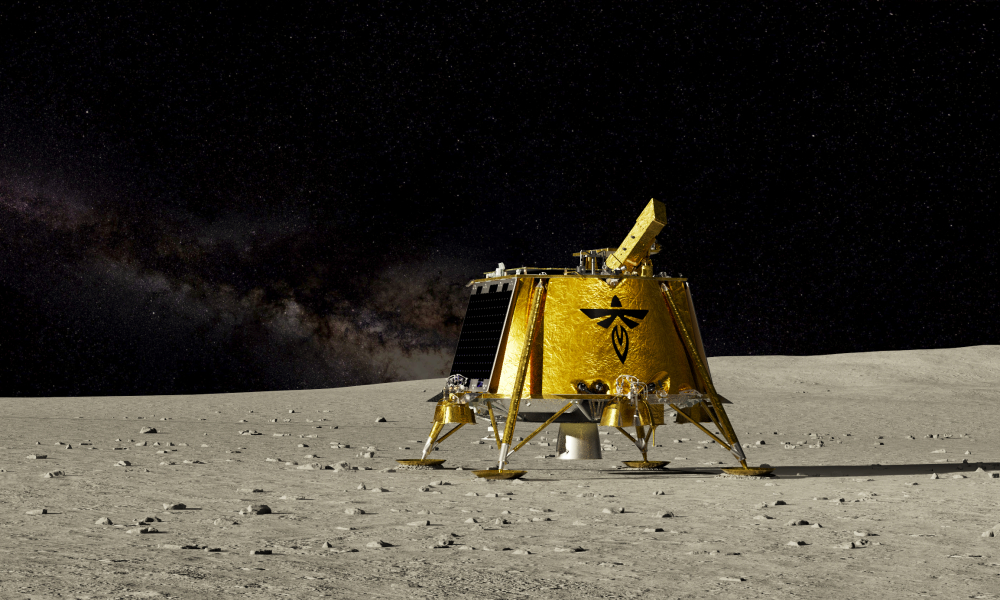

Firefly Aerospace is expanding access to low-cost, high-performance space launches with its “Alpha” and “Beta” rockets. It has also developed “Blue Ghost,” a lunar lander for NASA missions. Blue Ghost recently completed a huge milestone — firing up its engines to leave Earth orbit and begin its journey to the moon. This marked a significant step in Firefly’s role in lunar exploration and is definitely one to keep an eye on.
Howmet Aerospace
Howmet Aerospace is a global provider of advanced aerospace materials, supplying engine components, structural parts, and defense solutions. Howmet Aerospace specializes in high-performance alloys, coatings, and 3D-printed aerospace components. With growing demand for next-gen aircraft and hypersonic systems, Howmet Aerospace is positioned to continue advancing aerospace engineering and recently reported strong financial performance, with Q4 profits rising to $314 million from $236 million last year, surpassing market expectations.
What’s next for aerospace companies?
The aerospace industry is advancing quickly, with aerospace companies pushing forward in lunar exploration, asteroid mining, in-space manufacturing, and satellite deployment. Innovations in next-generation propulsion, reusable launch systems, and deep-space resource extraction are expanding access to space and redefining how materials and technology are developed beyond Earth.
Satellite and cargo deployment are becoming more flexible and efficient, improving space sustainability, national security, and responsive delivery systems. Missile defense is also emerging as a key priority, with companies shifting their focus to meet growing defense and security demands. With strong government contracts and commercial partnerships, aerospace companies are shaping the future of space and defense.
As these companies scale operations and tackle complex engineering challenges, many are adopting PLM software to streamline product development, improve collaboration, and enhance data management. By integrating PLM software into their workflows, aerospace companies can accelerate innovation to keep a competitive edge in an industry that demands both precision and speed every minute of the day.